When it comes to patient-centric healthcare, the laboratory plays a critical role, providing essential insights for physicians in disease diagnosis and treatment planning. With over 70% of clinical decisions relying on data received from the laboratory, the accuracy of test results is vital. 1
Understanding the importance of addressing pre-analytical errors is crucial in ensuring the delivery of high-quality patient care and upholding the integrity of diagnostic services. In this article, we delve into the complexities of pre-analytics, explore common errors, and discuss strategies for prevention.
Table of Contents
What is Pre-Analytics?
Pre-analytics refers to the first stage in The Total Testing Process which refers to the entire sequence of steps involved in laboratory testing, from the initial request for a test to the final interpretation of the test results by healthcare professionals.
This testing process can be divided into three distinct stages:
- Pre-analytical phase – involves all the processes that occur before the actual analysis of the sample.
- Analytical phase – this is where the actual testing or analysis of the sample takes place.
- Post-analytical phase – occurs after the analysis of the sample is completed. It involves result verification, interpretation and reporting.
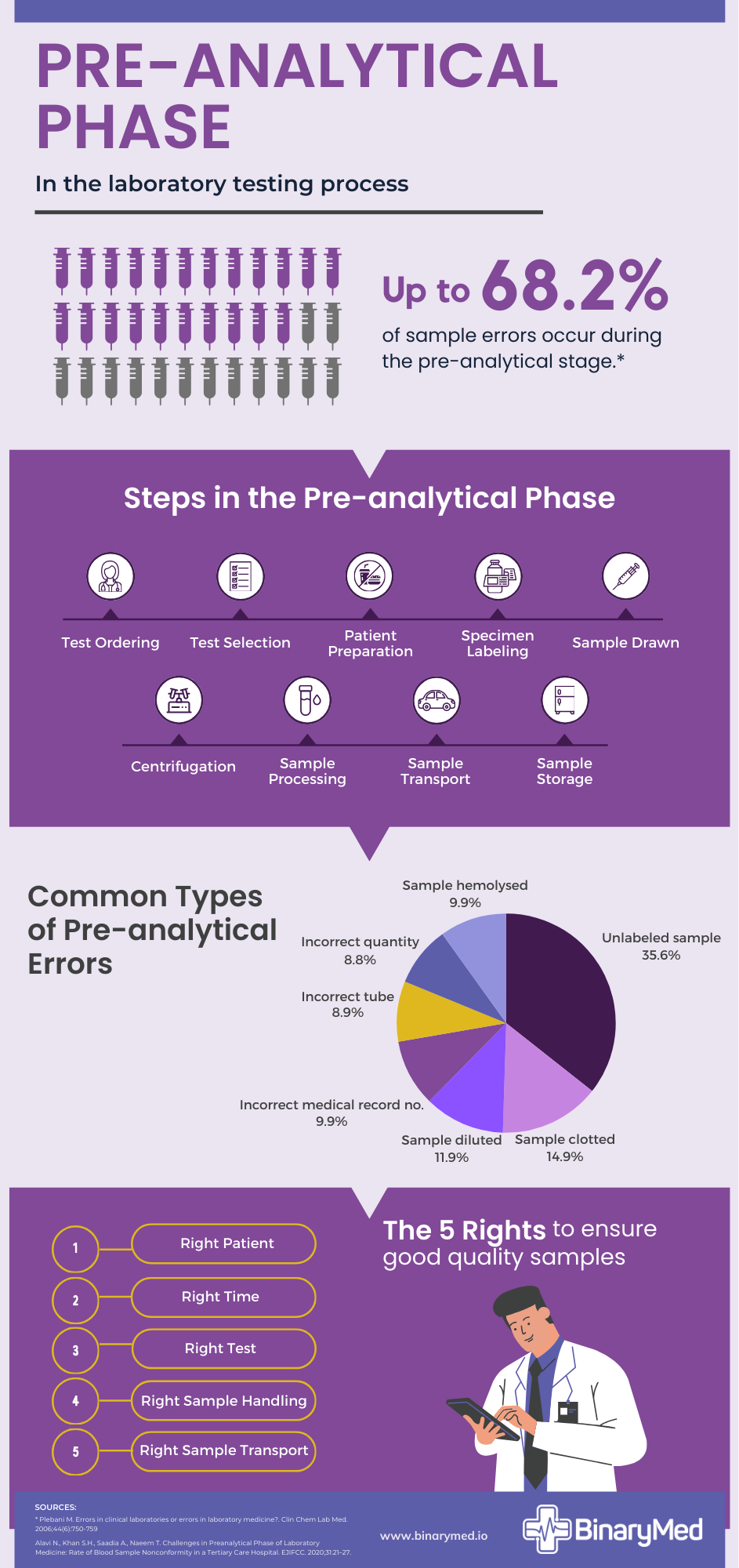
In addition to the above phases, the term “pre-pre-analytical phase” has also been created to split the pre-analytical phase into two distinct parts. 2 The pre-pre-analytical phase refers to the initial part of the pre-analytical stage before sample collection and includes activities such as test selection, test ordering and patient preparation.
Key Components of the Pre-Analytical Phase
The key tasks in this phase include:
- Test selection
- Test ordering
- Patient preparation
- Sample drawn
- Centrifugation
- Specimen labeling
- Sample transport
- Sample processing
- Sample storage
Each step is interconnected and plays a vital role in maintaining sample integrity and preventing errors that could compromise test results.

Common Pre-Analytical Errors
While each of the testing phases are equally important, the preanalytical phase stands out as the segment most susceptible to errors. In recent decades, preanalytical challenges have emerged among the highest number of obstacles encountered by laboratory professionals. 3
Studies show that the pre-analytical phase accounts for 46% to 68.2% of errors observed during the Total Testing Process. 4 Here is a list of the common pre-analytical errors:
- Unlabeled or mislabeled samples
- Clotted samples
- Diluted samples
- Incorrect medical record numbers
- Hemolysed samples
- Incorrect tubes used
- Incorrect sample volume
- Insufficient samples taken
- Improper sample handling
- Inadequate transportation and delays
As evidenced by the list above, numerous factors within the pre-analytical process can lead to errors. Issues such as mislabeling, improper sample handling, and delays in transportation can lead to sample degradation or contamination, resulting in inaccurate test results. 5
Pre-analytical errors have a direct impact on the accuracy and reliability of laboratory test results. Even minor deviations during sample collection or handling can introduce variability and bias, leading to erroneous interpretations and potentially incorrect diagnoses.
What impact do pre-analytical errors have on patient outcomes?
The consequences of pre-analytical errors extend beyond the laboratory, directly impacting patient outcomes. Pre-analytical errors can have significant implications for patient outcomes. Here are some of the impacts:
- Misdiagnosis: Errors in sample collection, labeling, or handling can lead to incorrect test results, potentially resulting in misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis of medical conditions.
- Inaccurate Treatment: Incorrect test results due to pre-analytical errors may lead to inappropriate or ineffective treatment plans, compromising patient care and outcomes.
- Patient Safety: Pre-analytical errors can pose risks to patient safety, especially if erroneous results lead to unnecessary procedures, treatments, or medications.
- Delayed Treatment: Any delay in obtaining accurate test results due to pre-analytical errors can delay necessary treatment interventions, allowing conditions to worsen over time.
- Financial Burden: Incorrect or delayed diagnoses resulting from pre-analytical errors may lead to increased healthcare costs for patients, as well as potential legal and financial repercussions for healthcare providers.
Overall, pre-analytical errors can undermine the quality of patient care, diminish patient trust in healthcare systems, and have far-reaching consequences for both individuals and laboratories.
How do pre-analytical errors affect laboratories?
Laboratories facing preanalytical errors can encounter several ramifications, including:
- Reputation Damage: Consistent preanalytical errors can tarnish the reputation of a laboratory, eroding trust among healthcare providers and patients.
- Legal Consequences: Errors in sample handling or labeling may lead to legal liabilities, including malpractice lawsuits or regulatory fines, particularly if patient outcomes are adversely affected.
- Financial Losses: Addressing preanalytical errors may require additional resources for retesting, sample recollection, or corrective actions, leading to increased operational costs and potential revenue loss.
- Quality Assurance Challenges: Preanalytical errors highlight weaknesses in quality assurance processes and may necessitate improvements in staff training, protocol adherence, and workflow optimisation.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Regulatory bodies may investigate laboratories with a history of preanalytical errors, potentially resulting in compliance audits, penalties, or license revocation.
In essence, addressing preanalytical errors is not only crucial for upholding patient safety, but also for maintaining the integrity of laboratory operations and trust in the healthcare system.
How can pre-analytical errors be prevented?
- Quality Assurance in Pre-Analytics To mitigate pre-analytical errors, laboratories can employ robust quality assurance measures. Standardised protocols, regular audits, and staff training programs are essential components of quality assurance initiatives aimed at maintaining high standards throughout the pre-analytical phase.
- Technological Innovations Advancements in technology have revolutionised pre-analytical processes, offering innovative solutions to minimise errors and improve efficiency. Automated specimen tracking systems, barcode labeling, and real-time monitoring tools enhance traceability and accountability, reducing the likelihood of errors.
- Best Practices for Specimen Handling Healthcare professionals can mitigate pre-analytical errors by adhering to best practices in specimen handling. Proper training, clear communication, and meticulous attention to detail are critical for ensuring sample integrity and minimising the risk of errors.
- Role of Education and Training Ongoing education and training are indispensable for healthcare staff involved in the pre-analytical phase. Continuous professional development ensures that personnel remain updated on the latest protocols, technologies, and best practices, empowering them to deliver high-quality patient care.
How BinaryMed assists in reducing pre-analytical errors?
BinaryMed offers an IoT (Internet of Things) solution designed to help laboratories reduce pre-analytical errors and enhance overall operational efficiency. Through our cutting-edge IoT technology, laboratories gain real-time visibility into tracking and monitoring of samples from collection centres to the laboratory.
Our solution provides instant alerts for temperature fluctuations, sample movement, and more, enabling prompt intervention to prevent errors before they occur.
Additionally, our web-based platform, the Binary Cloud, offers customisable alerts, detailed reporting, and seamless integration with existing laboratory systems, empowering healthcare professionals to streamline workflows and maintain high standards of quality assurance.
By leveraging BinaryMed’s comprehensive solutions, laboratories can minimise pre-analytical errors, improve patient care, and optimise laboratory performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of preanalytical errors on patients cannot be overstated. From delayed diagnoses to incorrect treatment plans, these errors directly affect patient outcomes and well-being.
Errors occurring in the preanalytical phase can undermine patient confidence in diagnostic services, tarnish the laboratory’s reputation, and result in heightened operational costs for both laboratories and hospitals. Addressing pre-analytical errors is paramount for improving patient outcomes and enhancing the quality of care.
Contact BinaryMed on [email protected] to learn more about how we can help you reduce pre-analytical errors and deliver reliable results for optimal patient outcomes.
References
- Datta P. Resolving discordant specimens. ADVANCE for Administrators of the Laboratory. July 2005:60
Prof.Dr. Plebani M. The emerging importance of the pre-pre-analytical phase in reducing testing errors and improving patient safety. Roche LabLeaders. Published July 17, 2023.
Simundic AM, Lippi G. Preanalytical phase – a continuous challenge for laboratory professionals. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2012;22:145-149
- Plebani M. Errors in clinical laboratories or errors in laboratory medicine? Clin Chem Lab Med. 2006;44(6):750-759.
- Alavi N., Khan S.H., Saadia A., Naeem T. Challenges in Preanalytical Phase of Laboratory Medicine: Rate of Blood Sample Nonconformity in a Tertiary Care Hospital. EJIFCC. 2020;31:21–27. Published 2020 Mar 20.

